What Prospectors need to know about Ground Mineralization
- Leend
- Jan 15, 2023
- 11 min read

Ground mineralization is a term used to describe the magnetic properties of the ground. This means that the ground has small pieces of metal or other materials that can cause a magnetic response.
Minerals in the ground are found all around us, and they play an important role in the environment. Minerals are made of atoms that are smaller than the atoms in plants and animals, and they are found in the Earth's crust and in the water that flows through the Earth. Minerals are important for plants and animals to eat, and they are also important for the Earth to keep its surface warm and dry.
Mineralization in soil can be a problem for gold prospectors, especially when hunting for treasure or Gold nuggets. This happens because the metal in the soil can cause sensitive detectors to start reacting.
Chapters
Indicators for highly mineralization soil?
Photos and examples of mineralized soil and rocks.
How does mineralization affect gold and metal detectors?
How prospectors overcome the soil mineralization problem.
Conclusion
Additional Info

What is Soil Mineralization?
Soil mineralization is a result of the magnetism in the soil. This magnetism can be caused by particles in the soil that have metal characteristics. This makes the soil's magnetic field strong and some detectors (like those used by successful gold miners) can pick up on those magnetic fields emitted by the soil.
When you're looking for treasure or artefacts, it can be hard to tell if your detector is reacting to the ground minerals or the intended target like a valuable relic. This means that even if you're looking in new territory, there's a chance you might not find anything because the ground is full of rocks with very high metal content causing your detector to work overtime. However, if you're detecting ground with lower levels of mineralization, metal detection is much easier. This is because the minerals can make the metal signals very faint and inaccurate.
The Earth's soil consists of sand, decomposed animal and plant material and various minerals. Some areas have a lot of minerals. These areas are known as highly mineralized areas and that is actually where Gold is usually found.
The mineralization is caused by its surface to be exposed to various conditions over extremely long time periods. Rain, floods and other natural occurrences helped to push iron containing compounds nearer to the surface. Or right to the surface (outcrops). That's good. Because Gold also is pushed to the surface in this fashion.
Erosion, glacial activity, activities and changes of waterways and other geological events create and change soil structures. That is a continuous process.
Types of Mineralization
Mineralization helps to make nutrients more available to the living beings. There are other types of mineralization than just ground mineralization. Minerals found in plants and water are further forms of mineralization.
Carbon dioxide becomes a solid mineral when it is converted into a carbonate.
Nitrogen mineralization is a process that helps us get nitrogen from dead organisms and from organic matter.
How does mineralization of soil occur?
Soil mineralization is the process of turning organic matter into other states such as gases, liquids or and minerals. There is a whole industry that has developed about carbon emissions where humans cause the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
I think it's safe to say that this is actually one of humanity's current major topics. Climate change and all. I dont go into whether or not it's man made or not. Different topic and the wrong place to discuss that.
Mineralization is a process that helps plants get nitrogen from the soil. The rate of mineralization depends on many factors such as
the temperature of the soil,
the amount of water it has,
the type of soil,
its pH.
Mineralization is slower in soils that are more acidic.

Three categories of oil organic matter:
the living biomass of microbes
fresh and partially decomposed detritus (rock fragments)
and humus.
More info about soils organic matter.
Why Nitrogen Levels Are Important
The nitrogen in the soil is important for plants. If the nitrogen in the soil is low plants will grow slowly or not at all. Low temperatures can slow down the process of nitrogen uptake.
Soil can become more mineralized by adding organic matter such as bean residues, dung and other natural organic fertilisers.
Mineralization and nitrogen levels can be affected by weather, such as rain or humidity. When it's wet outside, water can seep into the soil and dissolve minerals, which can then be lost through leaching. That is why the timing of fertilising activities is crucial to the maintenance of proper mineralization and nitrogen levels.
Effects of Agriculture on Soil
Soil is important for plants because it provides nutrients, moisture, and a place to grow. When plants grow, they take up space and reduce the amount of soil available for other plants. Crop residue, such as stalks, leaves, and husks, helps to reduce soil erosion and conserves water resources. In addition, residue management helps to improve soil quality and provide habitats for wildlife.
The amount of nitrogen in the soil has increased over time, which has affected plant growth patterns. Too much nitrogen can cause algae blooms and dead zones in lakes and ponds and it can also negatively affect native plants. Soil microbes play a key role in nutrient cycling and decomposition and their communities vary widely among soils and across space and time. This affects the unique soil microbial biomass of any soil sample.
Soil & Microorganisms
The soil is full of different kinds of microorganisms that work together to help decompose organic matter and hence make new soil. Microorganisms in the soil can also help to make the soil more fertile by converting nutrients. Some things that can affect the rate at which microorganisms decompose organic matter are the temperature, moisture, pH, and oxygen availability.
The microbial activity that occurs in soils converts organic matter into humus, which then releases carbon dioxide. Soils can have different characteristics that affect how much carbon dioxide is released.
Decomposition and the mineralization of organic carbon both play a role in the biogeochemical cycle, which is important for releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere and contributing to climate change. Global warming is also caused by this process, which releases methane.
Poor soil characteristics, like low pH values and a high amount of organic matter, as well as poor drainage, are all associated with soil degeneration.
Visual Indicators for Mineralization
New soil is generally of lower mineralization whereas highly mineralized soil tends to be red or reddish in colour. So that would give you a first clue on how to category soils.
Simple knowledge like this is very important for Gold prospectors.
Some metallic minerals in the soil can send false signals to metal detectors. This can make it difficult to find real treasure, because some things that might look like treasure may just be false signals caused by a rock with lots of metal contained in it. That's called hot rock. That metal could basically be any metall. Copper, iron, gold, manganese, lead etc etc..
High mineralization formations that Gold Prospectors need to know.
The types of rocks and formations that can contain gold vary widely and can occur in many different geologic settings. Some types of rocks that are commonly associated with gold deposits include:
Quartz veins - These are veins of mineralized rock that contain significant amounts of quartz, which can be gold-bearing.
Laterites - These are surface soils that have been weathered and altered by tropical weathering. They can be rich in bauxite, nickel, and gold.
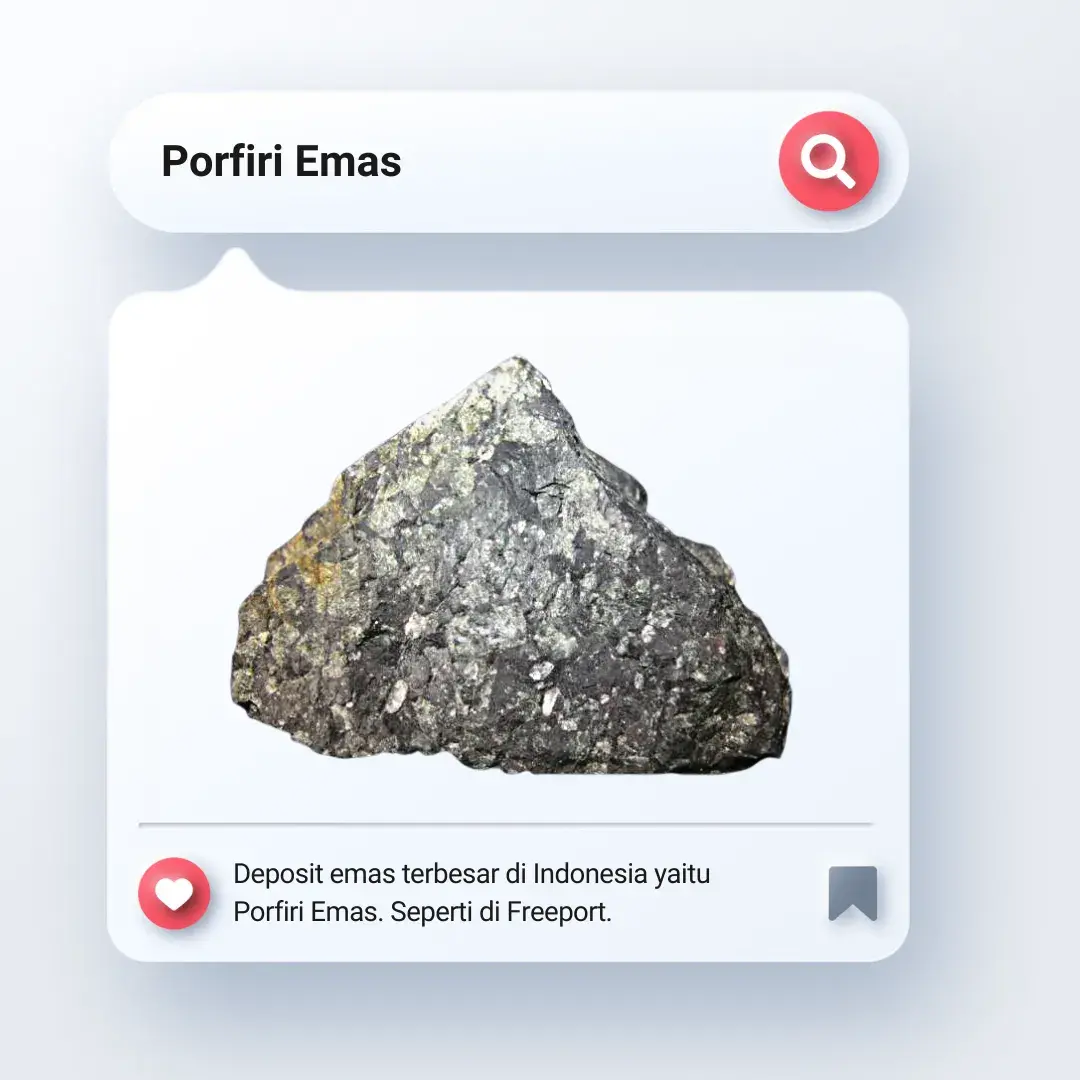
Porphyry - These are rocks that are formed from volcanic eruptions and can contain gold-bearing minerals such as copper and molybdenum.
Skarns - Skarns are metamorphic rocks that form around intrusive igneous rocks and can contain gold-bearing sulphides such as pyrite and arsenopyrite. Reference of Skarn Gold Picture.
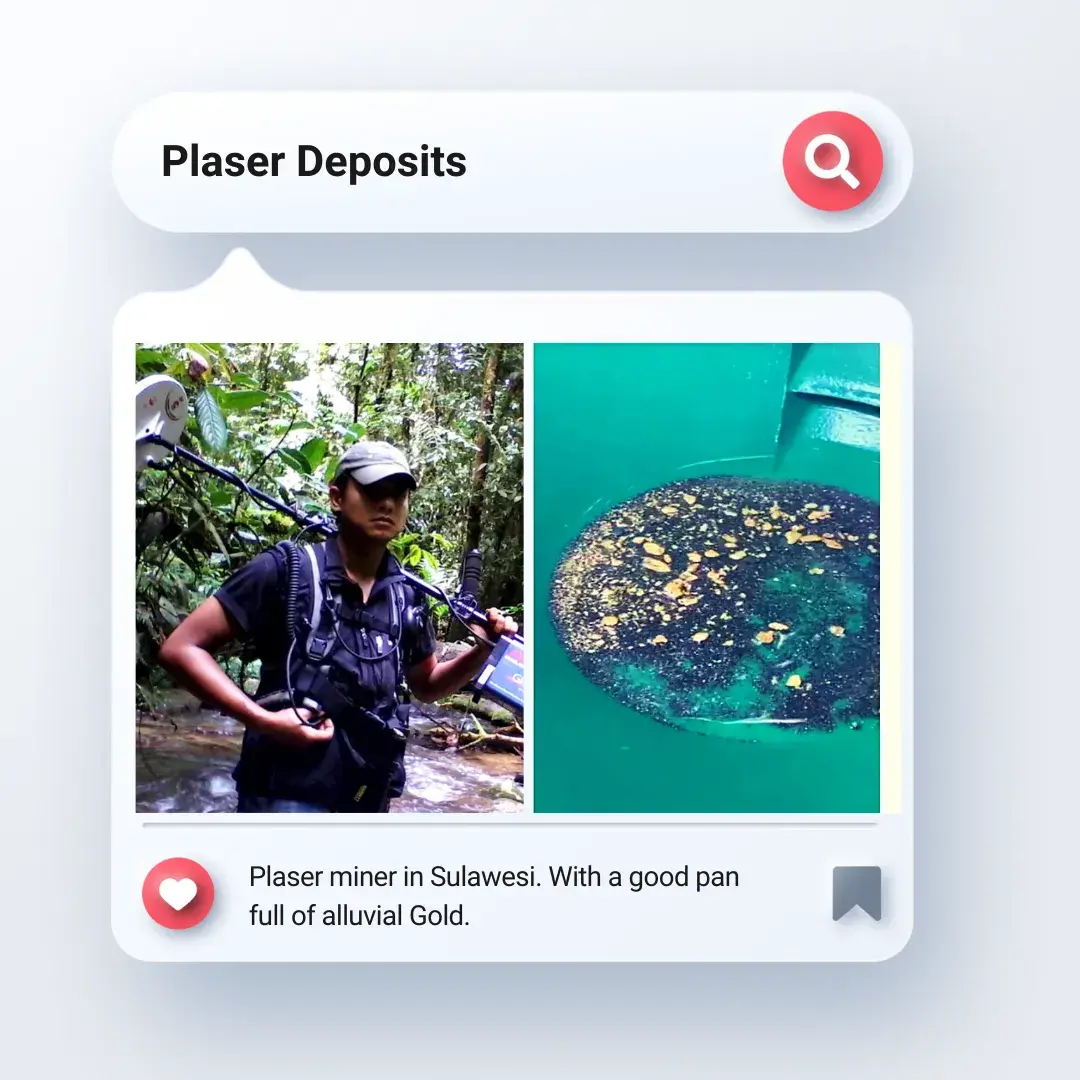
Placer deposits - These are gravel deposits that have been formed by the erosion and weathering of gold-bearing rocks.
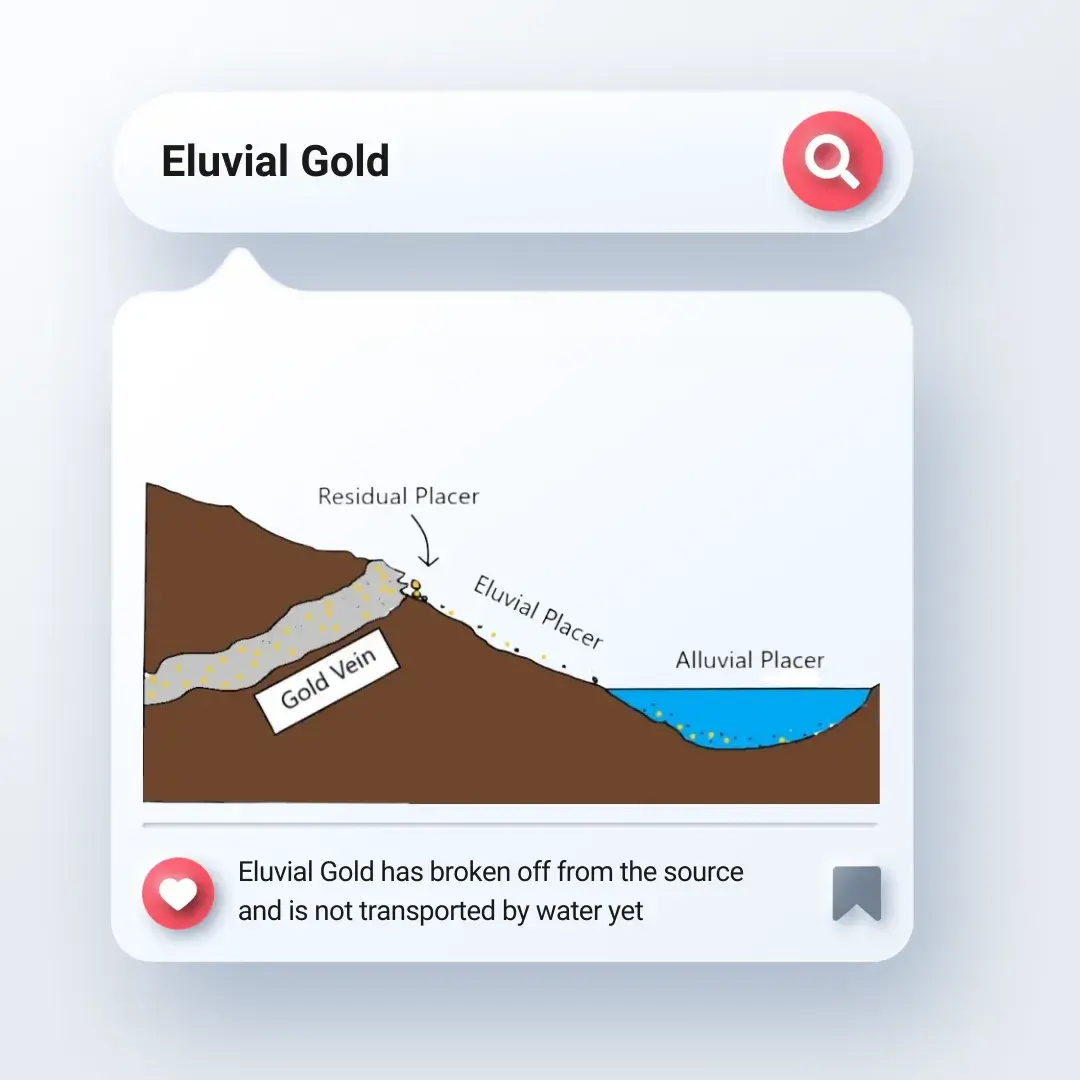
Eluvial deposit – Eluvial gold deposits accumulated through the process of weathering and erosion and can be found on the surface without any need of deep mining.
Gold nuggets - Nuggets are large pieces of gold that have been naturally transported by water or glacial ice and can be found in stream gravels or glacial till.
Many Ways How Mineralization Affects Us
Mineralization affects many different aspects of our lives including the entire agrarian sector all the way up to the building and infrastructure contractors. It's the minerals that provide the nutrients plants and livestock need to thrive. But it can give metal detectorists a hard time, especially if mineralization levels are high and the detectorist chose the wrong detector.
The metal detectors can detect different materials, but they can't detect things that are not made of metal. This is why if you find something that is metal, the detector will pick it up, but if you find something that is made of rocks or dirt, the detector usually won't pick it up except when the soil contains metallic minerals.
Archaeology & Treasure Hunting
Archaeologists use ground mineralization to find artefacts and other remnants of ancient times. If minerals have accumulated on the ground where an artefact might be, this can make it look like there is an object there when in fact it's just highly mineralized rocks and soil.
Infrastructure & Buildings
Infrastructure cannot be built in areas with high clay content as clay contains large amounts of water and is very heavy. Hence it may cause the ground to shift suddenly when surrounding material cannot withstand the weight or the water content in such clay changes. Such ground is not suitable for heavy infrastructure. That's just an example unrelated to metal detecting how mineralization affects us in daily life.
Agriculture
Same goes for agrarian activities. Farming means you need to take care of the soil and the nutrients contained in it. If the soil isn't healthy then it won't be able to support plants and farmers may need to use fertilisers. The four main minerals that soil needs are calcium, phosphor, boron and magnesium. If those are not available in sufficient quantities in the ground farmers need to use fertilisers.
There are various sectors and examples affected by such mineralization and soil types.
Metal Detecting and Ground Mineralization
Mineralization can affect how easy it is to find metal objects. Areas with a lot of minerals on the surface tend to be more difficult to work on due to the interferences such ground causes for detectors.
As stated above, red soil, which is usually indicative of high mineralization. It means that it may be more difficult to find objects made of metal, including Gold. Indonesia has extremely mineralized soil. That is why Indonesian soil is so fertile in the first place. But for Gold prospectors and treasure hunters this means they better revert to metal detectors with the capacity to handle such mineralization levels. No worries. There are such metal detectors.
How does mineralization affect the metal detector?
The mineralized ground has an electromagnetic field that is different from the fields around buried targets. The mineralized ground produces an X signal that is stronger than an X or R signal from a buried target.

This is because the body of mineralized ground is large and its field covers a large area. However, over short distances, the signals from mineralized ground and buried targets will be pretty similar to those caused by metal and Gold objects in the ground. And that is what can distract the metal detector.
How to solve the mineralization problem?
Ground Balancing Feature of Metal Detectors
Metal and Gold detectors come with a feature called ground balancing.This feature helps the detector to detect metal objects while ignoring or at least minimising the effects of mineralization in the ground. All detectors have this feature and ground balancing is either done manually or automatically.
It basically allows the detector to calibrate itself to the mineralization present in the ground and hence achieve adjusted reactivity to mineralization that would have caused interferences and false signals otherwise.
Read more Info about Ground Balancing.
The frequency of a metal detector signals the number of times per second that it sends and receives electrical impulses in the ground. This number is measured in kilohertz or kHz. Some metal detectors have frequencies that are higher than others, which is why you might see them work better in areas with more mineralization. And some detectors emit various frequencies at the same time which leads to a much better behaviour of the detector in such mineralized soils. It's more stable then.
Ground Tracking Feature: A Milestone in Detection Technology
With advancements in technology a new feature emerged which is ground tracking.
Ground tracking means that the detector has the ability to automatically adjust its ground balance as ground conditions change.
Ground tracking was first introduced by Jack Gifford of Tesoro Electronics in the Lobo model.
Ground tracking makes metal detecting much easier and renders even highly mineralized soils feasible grounds to use a gold detector. Basically all modern gold detectors and treasure detectors such as Gold Monster 1000, Goldmaster 24k, SDC2300, GPX6000, Equinox 900 and the Vanquish series do have a ground balancing and ground tracking feature.
Ground balance, especially when combined ground tracking, is an important feature for metal detectorists because it:
helps to eliminate false signals caused by mineralization in the ground and hot rocks.
improves detection depth and sensitivity by removing interference from the ground.
allows the detector to calibrate itself to the specific ground conditions and hence achieves more accurate and reliable results.
enables the detector to locate metal objects in areas with highly mineralized soil.
facilitates smoother and more efficient treasure hunting allowing detectorists to focus on finding valuable targets rather than constantly adjusting their detectors to changes of the ground.
Types of Metal Detectors Working in Highly Mineralized Areas
Pulse Induction (PI)
PI is a technology that is used in certain types and models of metal detectors. PI detectors are highly effective for hunting in mineralized soil conditions. Pulse Induction metal detectors work by emitting a powerful, momentary current that magnetises the ground. This current is powerful enough to penetrate through the mineralization, enabling the detector to measure the time to zero volts precisely, even in the absence of metal. By doing so, it helps to reduce or completely eliminate the impact of soil mineralization on its detection capabilities resulting in more accurate and reliable results.
One of the main practical advantages of PI technology is that it's highly immune to ground mineralization. This is extremely helpful when hunting in areas with high mineral content. Most other metal detectors are not able to handle such grounds effectively. Also, because of its immunity to mineralization, Pulse Induction detectors can detect deeply buried objects. Another practical advantage is that PI detectors are less likely to produce false signals, allowing the detectorist to focus on the target without being distracted. If you plan on doing serious metal detecting in highly mineralized ground, a pulse induction detector might be your best option.
Multi Frequency Detectors
Multi-frequency metal detectors are particularly useful for detecting metal and Gold objects in highly mineralized ground. This is because mineralization can cause interference with the signals emitted by the detector.
One way that multi-frequency detectors overcome this problem is by using multiple frequencies simultaneously. By using a combination of different frequencies the detector is able to better filter out the interference caused by mineralization and focus on the signals that are most likely to indicate the presence of metal.

Sumber: Minelab Multi IQ Paten
Another advantage of multi-frequency detectors is that they allow the prospector to adjust the settings to suit the specific conditions of the ground being searched. For example: in an area with high levels of mineralization, a lower frequency can be used to penetrate the ground more deeply and locate larger objects. In contrast, a higher frequency can be used to locate much smaller, shallower objects. Tiny Gold nuggets and flakes would be examples for that. Higher frequencies are more capable to pick up on the small Gold targets.
Multi-frequency detectors also have a better depth penetration than single frequency detectors.
Overall, multi-frequency detectors are an excellent choice for metal detector enthusiasts who are hunting Gold or treasure in highly mineralized ground. They offer a range of advantages over single frequency detectors, including better signal penetration and the ability to adjust the settings to suit the specific conditions of the ground.
Conclusion
I would go so far to say that Multi Frequency detectors are the new standard and that the majority of detectorists would be better off with a Multi Frequency detector. Especially when they are hunting in tropical and highly mineralized locations. Pulse Induction based and ZVT detectors best serve professional Gold prospectors. Multi Frequency detectors are best suited to overcome mineralization related problems when hunting for Gold and treasure. That especially applies to prospectors with limited experience, which is the majority.
There is a ranking of detectors for tropical areas such as Indonesia consisting of 3 models per detector class (professional, advanced, beginners). 9 detectors in total. The factor of mineralization was already considered when this ranking was conducted. Since we are in Indonesia, a tropical country with extremely high average mineralization, we automatically look at detecting from this particular ankle.
Feel free to read up on it: Top detectors for tropical locations.
Free Consultancy. Get in touch with us.


















Comentarios